Cardiovascular Disease and Chocolate
by ConstantineAug 12, 2023
Cardiovascular Disease and Chocolate PDF
Abstract
The antioxidants as polyphenols, especially flavanols present in cocoa, exert a favorable effect on endothelium vasodilation, modulate inflammatory markers, and decrease platelet aggregation, lipid oxidation and insulin resistance. Recent nutritional intervention trials and molecular studies demonstrate that consumption of cocoa, particularly rich in flavanols, is beneficial to promote cardiovascular health. This review describes the cardiovascular effects of chocolate.
1. Introduction
Chocolate, specifically dark chocolate, contains flavanols which have shown to increase endothelial nitric oxide formation promoting vascular health via vasodilation and blood pressure reduction (Persson IA, Persson K, Hagg S, et al. Effects of cocoa extract and dark chocolate on angiotensin-converting enzyme and nitric oxide in human endothelial cells and healthy volunteers-a nutrigenomics perspective. Journal of Cardiovascular harmacology.2011;57:44-50.) The most notable effects of chocolate on blood pressure reduction were seen in those patients with initially higher blood pressures and consumed the prescribed amount of chocolate for longer periods of time.
Additionally, one randomized control trial of 60 diabetic patients studied the effects of consuming 25g dark chocolate daily for 8 weeks and found, from the beginning to the end of the trial, a mean difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressures of -6.40 mmHg and -5.93 mmHg, respectively, whereas the control group of white chocolate consumption saw no significant difference.
1.2 Cholesterol
Many studies have been published regarding chocolate and its benefits on lipid profiles, the probable mechanism being a reduction of LDL oxidative effect and atherogenesis (Baba et al., 2007). A meta-analysis ... To accommodate for heterogeneity, this study evaluated the difference in post-intervention values of serum total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides, the interventions being chocolate consumption and the control treatments... The differences (95% CI) for total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides were ... highlighting a significant reduction in total cholesterol and LDL. This study also evaluated the effect of treatment duration on LDL and found significant reduction of ... after 2 weeks of treatment, but a non-significant reduction after 4 to 12 weeks of treatment. In accordance with this meta-analysis, a clinical trial studied the effects of a high polyphenol diet consisting of 50g of dark chocolate Regarding HDL cholesterol, another randomized, controlled, cross-over trial of 24 participants did find a statistically significant increase in HDL after consuming 30g of chocolate daily for 4 weeks (p < 0.001), contrary to the meta-analysis.
1.3 Arrhythmias
Chocolate consumption has been inconsistently associated with risk of atrial fibrillation...which indicates that no conclusive associations could be drawn from this study regarding chocolate consumption and risk of atrial fibrillation.
1.4 Coronary artery disease
Chocolate consumption has also been associated with reduced coronary artery disease (CAD) incidence and mortality (Baba et al., 2007; Persson et al., 2011). A systematic review by Kwok et al, pooled data from nine studies with 157,809 participants and follow-up durations of 8-16 years studied chocolate consumption and CAD. They performed a met-analysis on data from five of the studies which demonstrated, after propensity score matching, a significant association between chocolate consumption and reduced risk of CAD ... (Kwok et al., 2015).
1.5 Heart failure
Chocolate consumption may also lower the risk of heart failure (HF) by mitigating the risk factors of HF which include hypertension, CAD, and myocardial infarction.
1.6 Cerebrovascular accidents
Chocolate consumption is also associated with lower stroke incidence and mortality according to the meta-analysis by (Kwok et al., 2015). The meta-analysis evaluated five prospective cohort, and found that after adjusting for other possible covariates, chocolate consumption significantly decreased risk of both stroke incidence ... and stroke mortality.
1.7 Peripheral vascular disease
Dark chocolate is also thought to improve outcomes in patients with peripheral arterial disease,
2. Discussion
The studies reviewed show that moderate consumption of
chocolate is beneficial for a variety of conditions including hypertension, cholesterol, coronary heart disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular accidents and peripheral vascular disease. Summary is demonstrated in Table 1.
Dark chocolate is preferred over white or milk chocolate because of the higher flavonol content. Serving size of 50 g once a day or once every other day have been shown to help with all these conditions. Upon consuming more than ten servings per week, adverse outcomes begin to be observed such as increased risk of HF.
Conclusion
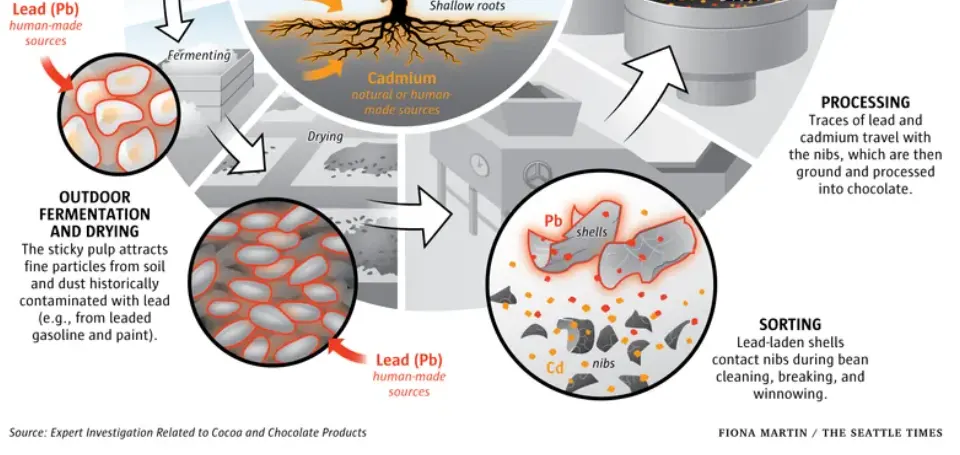
Serving sizes are shockingly ridiculous. With our under-processed healthy chocolate we recommend 1 gram square (3/8" x 1/2") using mouth-melt method after meals, 3 grams a day while the researchers say up to 50 grams a days is okay. Lead in dark chocolate is scandalous.
Next week we'll write about the type of chocolate the researchers are using.
TL;DR: ...promoting vascular health via vasodilation and blood pressure reduction ... ranging from an average of 1.4 to 105 grams of chocolate (30 to 1218 mg of flavanols per day.

 Break bar horizontally across four squares, then break vertically for a single dose square. Place the square on the roof of your mouth hold with tongue, let it melt for four minutes. Experience
Break bar horizontally across four squares, then break vertically for a single dose square. Place the square on the roof of your mouth hold with tongue, let it melt for four minutes. Experience  This
This  Question Chatgpt:
Question Chatgpt: 


 Here is @egrazener partner in crime @discoverchoc aka Clay Gordon
Here is @egrazener partner in crime @discoverchoc aka Clay Gordon
 Here are a few articles about us in the 'real world.'
Here are a few articles about us in the 'real world.'